THE MAGIC
THE FORMULA
Code size has big impact on performance. The CPU has to read in the instructions before they are executed, a fact often neglected by programmers.
- It's 10 times faster to run 10 KB code than 100 KB code.
- The code size also have a direct impact on the CPU cache hit rate.
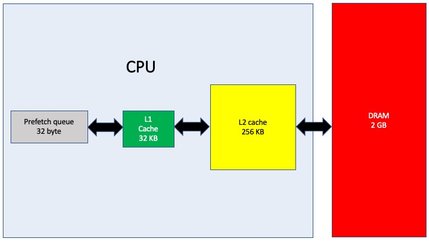
As DRAM is slow compared to the internal CPU cycle, caches are used to improve performance.
The illustration describes the Intel E3826 Atom processor.
Assume the following:
- All DRAM is used and 400 MB is code.
- L1 cache is 50 times faster than DRAM.
- L2 cache is 20 times faster than DRAM.
We want all the code we are executing in the L1 cache for maximum performance. The second best is the L2 cache. We have a problem though, as only fragments of the code will fit in the caches.
Larger code size cause higher cache miss rates which is very expensive for the performance.
The CPU executes the following steps to prefetch the code fragment.
- Search L1 cache. If found goto step 2 else goto step 3.
- Copy the fragment to prefetch queue and prepare for execution.
- Search L2 cache. If found goto step 4 else goto step 5.
- Copy the fragment to L1 cache and goto step 2.
- Copy the fragment from DRAM to L2 cache and goto step 4.
On a cache update, another code fragment must be evicted to create place for the new fragment. These operations takes time.
Thus quality (minimum size) versus quantity (bloatware) pays off big time in performance, power consumption and cost.
FEATURES
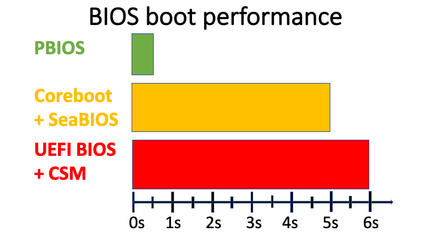
PBIOS
- Fast boot.
- PDOS integrated.
PDOS
- Designed from scratch to be used in embedded systems.
- Integrated support for standard PC, USB, eMMC and SD card devices despite a kernel size of only 150 KB.
- A graphics engine for image and raster operations is also integrated.
- CPU's in multi processor versions are run early in the OS initialisation process to take advantage of the parallelism.
- No headache of trimming the elephant as it's slimmed to a minimum right out of the box.
- The philosophy is to add the functionality you need instead of the error phrone mission of removing the ones you don't need.
- Handles the application workload at 1/5 of the cost of the hardware required for an open source OS.
- Should be regarded as a part of the hardware BOM (Bill Of Materials) as it's integrated in the BIOS.
PFAT
Microsoft FAT12, FAT16 and FAT32 are the most widely supported file systems in the industry. Volumes created by PFAT algorithm are 100% compatible with those file systems and has the following features:
- Expands FAT32 limit from 32 GB to 2 TB.
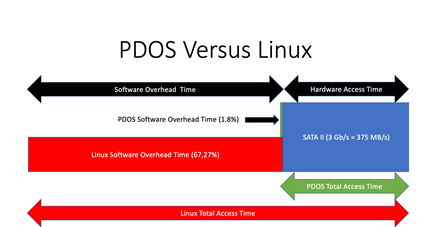
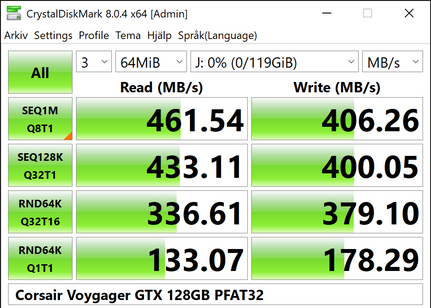
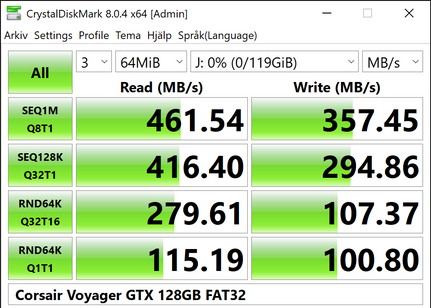
- 10% average improvement on FAT32 reads.1 Up to 2 times faster reads on SSD benchmarks.
- 95% average improvement of FAT32 writes.1 Up to 3.3 times faster writes on SSD benchmarks.
- Faster than NTFS.1
- Same speed as exFAT, but single volume instead of multi partition.1
- Enables USB and SD card drives over 32 GB size to remain removable drives.
- Cheaper than exFAT.
1Computed from Corsair Voyager GTX 128 GB benchmark.